# Adversarial Attack on Graph Neural Networks
# Attack type
# Evasion Attack:
- Definition: Evasion attacks, also known as adversarial examples, aim to manipulate the input data in a way that causes misclassification or incorrect output from a machine learning model. Evasion attack refers to attackers, without altering the target machine learning system, completing deceptive attacks on the target system by constructing specific input samples.
- Objective: The primary objective is to create inputs that are designed to be misclassified by the model, leading to incorrect predictions.
- Example:
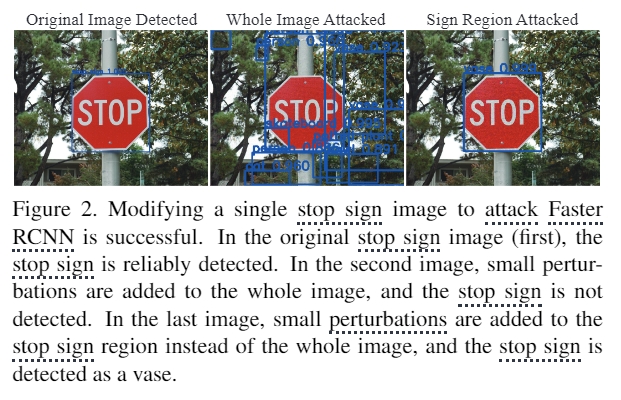
Causing Autonomous Vehicles to Misidentify Road Signs:In the original stop sign image (left), the stop sign can be successfully detected. In the middle image, with small disturbances added throughout the entire image, the stop sign cannot be detected. In the last image, with small disturbances added to the symbol area of the stop sign rather than the entire image, the stop sign is detected as a vase.
Deceiving Facial Recognition Systems: In a paper from CMU, wearing specially designed glasses can trick even the most advanced facial recognition software. These glasses not only make the wearer disappear from artificial intelligence recognition systems but also cause AI to mistake the wearer for someone else. Considering the widespread application of facial recognition systems today, the consequences could be dire if this method is maliciously exploited.

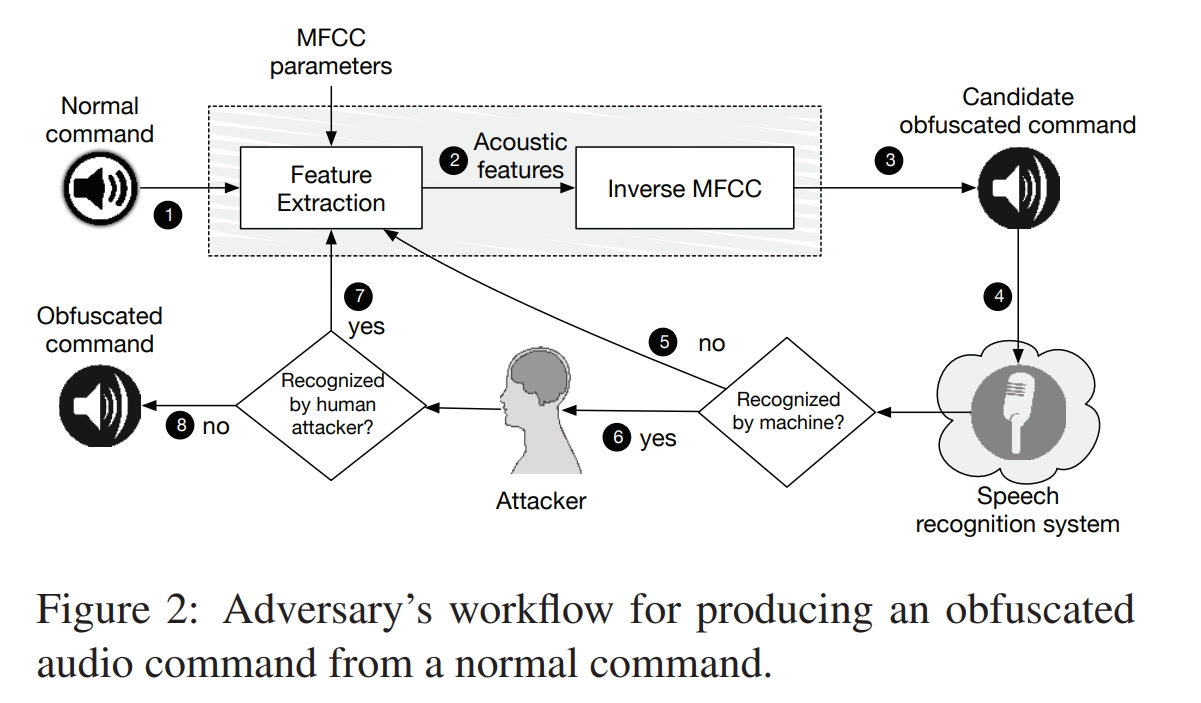
Attacking Speech Recognition Systems: Generating audio commands that create confusion by reverse engineering normal commands (such as a segment of noise indistinguishable by humans), causing them to be correctly recognized as corresponding voice commands on Samsung Galaxy S4 and iPhone 6. This manipulation leads to actions like switching the phone to flight mode or dialing emergency services.
# Backdoor Attack:
- Definition: Backdoor attacks involve the intentional insertion of a hidden pattern or trigger during the training phase, causing the model to behave unexpectedly when exposed to specific inputs during deployment.
- Objective: The attacker aims to create a "backdoor" that can be exploited to manipulate the model's predictions under certain conditions.
- Example: Training a face recognition model with a hidden trigger that causes misidentification when a specific pattern is present in an image.
# Poisoning Attack:
- Definition: Backdoor attacks involve the insertion of a hidden pattern or trigger into a machine learning model during the training phase. This trigger, known as a "backdoor," can be exploited to produce specific outputs when a particular, often rare, input pattern is present.
- Objective: Backdoor attacks aim to compromise the model's behavior in a targeted manner, usually without affecting its overall performance on regular data.
